Page 192 - CW E-Magazine (13-8-2024)
P. 192
Special Report
the point where a coloured oxide layer the surface. Some chelants also claim ledge and systems, and is less standar-
can be seen, there is a chromium to do this. dized than theother methods. The suc-
depleted layer on the surface of the cessful use of these systems needs to be
steel underneath the oxide layer. The Common passivation treatments established on a case-by-case basis.
lower chromium content causes lower include HNO solutions or pastes, which
3
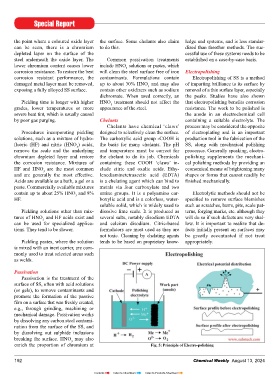
corrosion resistance. To restore the best will clean the steel surface free of iron Electropolishing
corrosion resistant performance, the contaminants. Formulations contain Electropolishing of SS is a method
damaged metal layer must be removed, up to about 30% HNO and may also of imparting brilliance to its surface by
3
exposing a fully alloyed SS surface. contain other oxidizers such as sodium removal of a thin surface layer, especially
dichromate. When used correctly, an the peaks. Studies have also shown
Pickling time is longer with higher HNO treatment should not affect the that electropolishing benefits corrosion
3
grades, lower temperatures or more appearance of the steel. resistance. The work to be polished is
severe heat tint, which is usually caused the anode in an electrochemical cell
by poor gas purging. Chelants containing a suitable electrolyte. The
Chelants have chemical ‘claws’ process may be considered the opposite
Procedures incorporating pickling designed to selectively clean the surface. of electroplating and is an important
solutions, such as a mixture of hydro- The carboxylic acid group -COOH is production tool in the fabrication of the
fluoric (HF) and nitric (HNO ) acids, the basis for many chelants. The pH SS, along with mechanical polishing
3
remove the scale and the underlying and temperature must be correct for processes. Generally speaking, electro-
chromium depleted layer and restore the chelant to do its job. Chemicals polishing supplements the mechani-
the corrosion resistance. Mixtures of containing these COOH ‘claws’ in- cal polishing methods by providing an
HF and HNO are the most common clude citric and oxalic acids. Ethy- economical means of brightening many
3
and are generally the most effective. lenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) shapes or forms that cannot readily be
Acids are available as a bath, a gel or a is a chelating agent which can bind to finished mechanically.
paste. Commercially available mixtures metals via four carboxylate and two
contain up to about 25% HNO and 8% amine groups. It is a polyamino car- Electrolytic methods should not be
3
HF. boxylic acid and is a colorless, water- specified to remove surface blemishes
soluble solid, which is widely used to such as scratches, burrs, pits, scale pat-
Pickling solutions other than mix- dissolve lime scale. It is produced as terns, forging marks, etc. although they
tures of HNO and HF acids exist and several salts, notably disodium EDTA will do so if such defects are very shal-
3
can be used for specialized applica- and calcium disodium. Citric-based low. It is important to realize that de-
tions. They tend to be slower. formulators are most used as they are fects initially present on surfaces may
not toxic. Cleaning by chelating agents be greatly accentuated if not treat
Pickling pastes, where the solution tends to be based on proprietary know- appropriately.
is mixed with an inert carrier, are com-
monly used to treat selected areas such
as welds.
Passivation
Passivation is the treatment of the
surface of SS, often with acid solutions
(or gels), to remove contaminants and
promote the formation of the passive
film on a surface that was freshly created,
e.g., through grinding, machining or
mechanical damage. Passivation works
by dissolving any carbon steel contami-
nation from the surface of the SS, and
by dissolving out sulphide inclusions
breaking the surface. HNO may also
3
enrich the proportion of chromium at Fig. 5: Principle of Electro-polishing
192 Chemical Weekly August 13, 2024
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised