Page 189 - CW E-Magazine (13-8-2024)
P. 189
Special Report
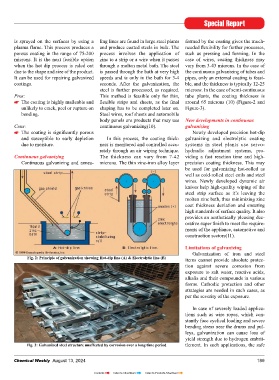
is sprayed on the surfaces by using a ling lines are found in large steel plants formed by the coating gives the much-
plasma flame. This process produces a and produce coated steels in bulk. The needed flexibility for further processes,
porous coating in the range of 75-200 process involves the application of such as pressing and forming. In the
microns. It is the next feasible option zinc to a strip or a wire when it passes case of wires, coating thickness may
when the hot dip process is ruled out through a molten metal bath. The steel vary from 3-43 microns. In the case of
due to the shape and size of the product. is passed through the bath at very high the continuous galvanizing of tubes and
It can be used for repairing galvanized speeds and is only in the bath for 3-4 pipes, only an external coating is feasi-
coatings. seconds. After the galvanization, the ble, and the thickness is typically 12-25
steel is further processed, as required. microns. In the case of semi-continuous
Pros: This method is feasible only for thin, tube plants, the coating thickness is
The coating is highly malleable and flexible strips and sheets, as the final around 65 microns (10) (Figure-2 and
unlikely to crack, peel or rupture on shaping has to be completed later on. Figure-3).
bending. Steel wires, roof sheets and automobile
body panels are products that may use New developments in continuous
Cons: continuous galvanizing(10). galvanizing
The coating is significantly porous Newly developed precision hot-dip
and susceptible to early depletion In this process, the coating thick- galvanizing and electrolytic coating
due to moisture. ness is monitored and controlled accu- systems in steel plants use servo-
rately through an air wiping technique. hydraulic adjustment systems, pro-
Continuous galvanizing The thickness can vary from 7-42 viding a fast reaction time and high-
Continuous galvanizing and annea- microns. The thin zinc-iron alloy layer precision coating thickness. This may
be used for galvanizing hot-rolled as
well as cold-rolled steel coils and steel
wires. Newly developed dynamic air
knives help high-quality wiping of the
steel strip surface as it’s leaving the
molten zinc bath, thus minimizing zinc
coat thickness deviation and ensuring
high standards of surface quality. It also
provides an aesthetically pleasing dec-
orative super finish to meet the require-
ments of the appliance, automotive and
construction sectors(11).
Limitations of galvanizing
Galvanization of iron and steel
Fig. 2: Principle of galvanization showing Hot-dip line (A) & Electrolytic line (B) items cannot provide absolute protec-
tion against severe corrosion from
exposure to salt water, reactive acids,
alkalis and their compounds in various
forms. Cathodic protection and other
strategies are needed in such cases, as
per the severity of the exposure.
In case of severely loaded applica-
tions such as wire ropes, which con-
stantly face cyclical loading and severe
bending stress near the drums and pul-
leys, galvanization can cause loss of
yield strength due to hydrogen embrit-
Fig. 3: Galvanized steel structure unaffected by corrosion over a long time period tlement. In such applications, the safe
Chemical Weekly August 13, 2024 189
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised